In the early part of 2020, a perplexing interruption in the conventional pedagogical process left global educational establishments flabbergasted. Among this turmoil was Rangiora High School, a beacon of New Zealand’s education system. They too had to face the burstiness of this sudden upheaval that brought traditional learning to an abrupt halt. The catalyst for this unexpected intermission was none but the emergence of COVID-19 pandemic – a worldwide health emergency that blurred lines between reality and dystopian fictions.
In no time, what initially appeared as an obscure virus from unfamiliar terrains morphed into a global disaster instigating countrywide confinements. With COVID-19 proliferating at such alarming rates, maintaining relentless vigil became paramount. As an integral part of this defensive schema, there arose an inevitable need to seal off Rangiora High School temporarily. This decision compelled students and staff alike – without forewarning or gradual transition – to abandon their customary routines and physical classrooms; thus heralding the start of a turbulent voyage towards remote learning.
Impacts of the Unanticipated Shutdown
The abrupt halting of conventional in-person education, triggered by an unpredictable shutdown, instigated a plethora of consequential repercussions. It coerced students and educators worldwide to acclimate to an unfamiliar state of affairs, interrupting the steady cadence of academia and hurling various challenges into the realms of learning, teaching and administration. Pre-existing educational structures were turned topsy-turvy, igniting a domino effect that transformed every fundamental element – from distributing knowledge to evaluation methods.
The perpetuation of learning was one area profoundly impacted by this unforeseen mutation. With physical classrooms suddenly out-of-bounds, both pupils and educators found themselves tentatively navigating through uncharted territory – remote learning. The transition not only caused turbulence in their daily routines but also resulted in academic progress slowing down, affecting the intellectual maturation and growth of students. Additionally, vital support services crucial for effective teaching-learning processes took a hard hit as well further emphasizing the brutal consequences brought on by this unexpected closure.
The Shift to Remote Education
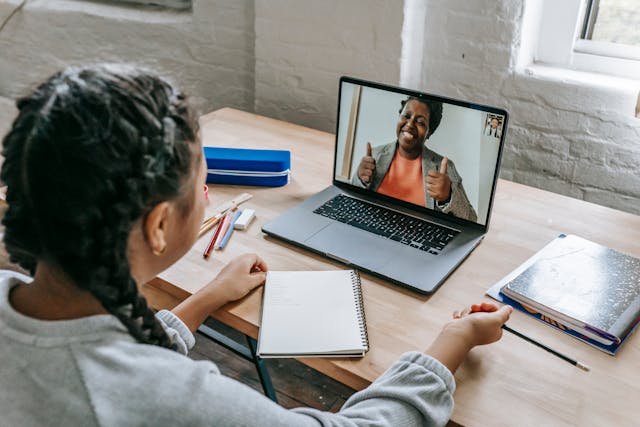
In the throes of the escalating global pandemic, educational institutions worldwide found themselves compelled to radically transform their teaching methods in a heartbeat. The age-old physical classrooms were replaced by virtual learning spaces as keeping distance became a critical necessity. Amidst this maelstrom created by the virus, technology emerged as an illuminating beacon of hope, enabling countless pupils to persist on their academic path. In response to this sudden shift, schools began employing various remote education tools like Google Classrooms, Microsoft Teams and Zoom for propelling their digital scholastic endeavors.
Nonetheless, swapping person-to-person instruction with a digital interface proved more complex than anticipated. Educators – many being adherents of orthodox pedagogical techniques – found themselves embarking on an uncharted expedition into the realm of online teaching. A formidable task lay before them: transmuting their curriculum into an internet-friendly format which demanded substantial time and exertion. Meanwhile, students grappled with adapting to this newfangled mode of learning; particularly those bereft of reliable internet connectivity or requisite gadgets faced severe hurdles. This abrupt switch shed light upon a deep-seated digital disparity that persists as a major impediment towards fair and equal education access.
Challenges Faced by Students and Staff During the Closure
As the global lockdown mandated a swift pivot to remote education, both students and staff found themselves navigating an uncharted territory fraught with unforeseen hurdles. This abrupt shift was not without its share of dilemmas that went beyond mere technological impediments.
Students, groomed in an environment rife with classroom kinetics, immediate interactions and tactile resources, were thrust into a disconcertingly complex transition. The sudden change weighed heavily on their motivation and engagement levels. Furthermore, they had to grapple with issues like unreliable internet connectivity and inadequate study spaces at home – factors that negatively impacted their learning experience.
Meanwhile, educators found themselves wrestling with their unique set of challenges. Habituated to traditional teaching methods, they were now tasked with acquainting themselves with digital platforms while crafting content apt for online pedagogy. They needed to adopt novel approaches for virtual interaction as well as repeatedly reassess their strategies to ensure academic continuity even while managing personal obligations under lockdown constraints.
The unexpected shuttering of educational institutions thus cast long shadows of significant difficulties over the lives of both students and staff.
Adapting to Digital Platforms for Learning

As if propelled by unseen forces, the sudden metamorphosis from conventional classrooms into the realm of digital education has mandated a swift embrace of electronic platforms for pedagogical tasks. This unexpected plunge into e-learning has thrust both teachers and students headlong into unfamiliar technological territory. The spectrum of these platforms stretches wide, spanning from live Zoom lessons, to assignments posted on Google Classroom, to lectures archived on YouTube – marking an unprecedented shift in how knowledge is imparted. These uncharted waters have proved both testing and transformative simultaneously; unveiling a new horizon in global academia.
On one side of the coin, these telematic platforms act as sturdy bridges over physical barriers allowing continuity in learning – a beacon amidst current times. Nestled within them lies potentiality for groundbreaking teaching techniques and advanced learning methods that could pave way for significant strides in educational technology. However, flipping this coin uncovers another narrative where educators are compelled to sprint across steep tech-learning slopes to ensure uninterrupted lesson delivery. Besides this, it’s also become crucial for pupils from diverse socio-economic strata to possess devices coupled with reliable internet connectivity – thus creating yet another hurdle while adapting to e-learning tools.
Despite such stumbling blocks being scattered across our path towards virtual education transformation, mastering these platforms’ functionality has emerged as an unforeseen yet indispensable skill-set within modern-day scholastics.
Maintaining Student Wellbeing and Mental Health
In the unforeseen throes of school closures and a swift transition to remote education, there has been an unmistakable surge in concern for student wellbeing and mental health. The labyrinth of distance learning doesn’t merely pose scholastic hurdles but also potentially unearths feelings of isolation, stress, and anxiety among students. A stark absence of direct interaction with peers and faculty can amplify these emotional tribulations.
Thus, it becomes vital – nay imperative – for educational institutions to weave threads of mental health support into their online tapestry. Schools carry the onus to engineer robust communication networks that provide students with platforms where they can air their anxieties and fears without hesitation.
Moreover, schools must not only incorporate mental health components within their curriculum but also extend supplementary resources like counselling sessions, workshops, and online webinars that focus primarily on managing stress and anxiety while fostering overall wellbeing. In this climate of uncertainty engendered by the pandemic times we find ourselves in – cultivating resilience amongst our learners is paramount.
Furthermore, dedicated efforts towards implementing such programs effectively along with promoting them enthusiastically combined with regular check-ins from teachers can do more than just maintain student’s mental well-being; it has potential to significantly enhance it thereby paving a smoother path towards empowering learning journeys laden with fruitful outcomes.
Here are some key strategies that schools can adopt to maintain and enhance student wellbeing and mental health:
- Establishing a robust communication network: Schools should ensure that students have an accessible platform where they can express their concerns, anxieties, and fears without hesitation. Regular check-ins from teachers or mentors could be beneficial in this regard.
- Incorporating mental health components within the curriculum: This approach not only educates students about mental health but also provides them with practical coping mechanisms. It is important for these topics to be discussed openly, thereby reducing stigma around them.
- Providing supplementary resources: Counselling sessions, workshops, online webinars focusing on managing stress and anxiety can greatly assist students during challenging times. These resources should be easily available to all students irrespective of their geographical location or financial constraints.
- Promoting resilience-building programs enthusiastically: Resilience helps individuals bounce back from adversity stronger than before. Hence, promoting such programs among learners will equip them with the necessary skills to navigate through uncertain situations effectively.
- Implementing regular teacher-student interactions: Teachers play a crucial role in shaping a student’s mentality towards learning as well as life challenges. They must regularly interact with each student individually – understanding their unique needs and providing tailored guidance accordingly.
- Encouraging peer interaction virtually: In absence of direct physical interaction due to remote learning circumstances – schools should encourage virtual group activities or discussions which would help alleviate feelings of isolation among students while fostering camaraderie amongst peers.
In essence, maintaining student wellbeing requires concerted efforts from educational institutions along with active participation from parents/guardians at home front too; creating a supportive environment conducive for holistic development of young minds amidst pandemic times we’re navigating through currently.
Effects on the Academic Calendar and Curriculum
The abrupt shutting down of educational institutions worldwide ushered in a seismic shift to academic timelines and syllabi. Academic calendars, typically delineated with specific periods for learning, evaluations and vacations, experienced an abruption due to the pandemic’s upheaval. Suddenly, the learning duration was unexpectedly curtailed; assessments either got cancelled or pivoted to digital platforms; the year’s chronology spiralled out of control – leaving schools grappling not just with lockdown restrictions but also its ripple effects.
In tandem with these alterations came a coerced departure from traditional pedagogical models. Educational content underwent radical overhauls to fit into virtual platforms while often being truncated to comply with revised academic schedules. This compulsory metamorphosis in pedagogic methods saw crucial educational elements such as practical workshops and extraction skills compromised as educators grappled with adapting their lectures for online delivery.
Essentially, the sudden standstill triggered by the health crisis caused turbulence both within academic calendars and curriculum structures necessitating swift strategy revisions and an immediate overhaul of conventional educational practices.
FAQ
The abrupt disruption catapulted students and staff into a state of bewilderment regarding their imminent academic roadmap, leading to an urgent transition from brick-and-mortar classrooms to virtual ones.
The unforeseen cessation triggered instantaneous shutdowns, interrupting ongoing studies and causing delays in the academic timeline. This presented a myriad of complexities concerning student evaluation, curriculum completion, and preparedness for remote learning infrastructure.
Transitioning towards distance learning involved embracing digital platforms for instruction delivery, modifying teaching methods, offering scheduling flexibility and introducing transformative assessment techniques.
Learners and instructors wrestled with numerous issues such as internet connectivity problems, unfamiliarity with digital instructional tools, maintaining focus in a home environment along with challenges associated with mental health preservation.
Academic bodies expeditiously incorporated online instructional platforms whilst training students as well as staff members. They also restructured their syllabi to fit into cyberspace instruction models while employing innovative assessment mechanisms.
Educational entities proactively furnished resources aimed at promoting mental health support while endorsing regular virtual social interactions – all in an effort to maintain equilibrium. Furthermore they provided curriculum flexibility alongside counseling services aiding students navigate through this period successfully.
Pandemic-induced disruptions led not only significant lags engulfing academia’s schedule but also necessitated complete overhaul of study material to adapt it for online learning environment. Examinations were deferred and the ensuing academic year started late.













+ There are no comments
Add yours